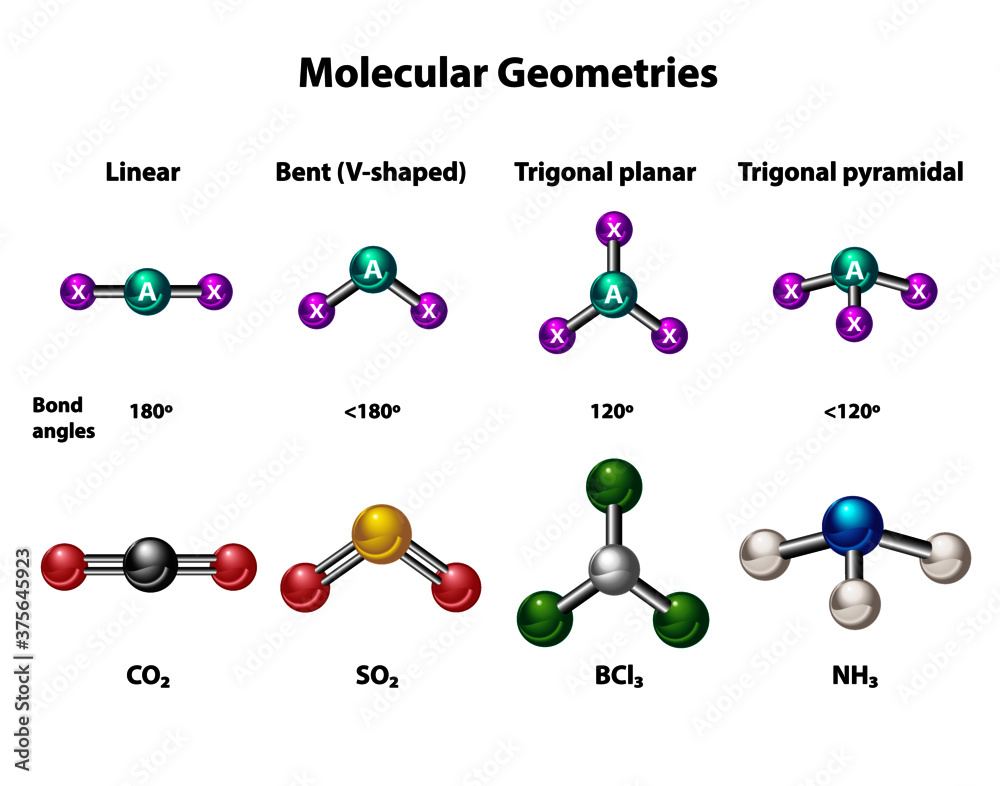
An example of trigonal pyramid molecular geometry that results from tetrahedral electron pair geometry is nh 3. The nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and thus needs 3 more. Scientists have been inspired to explore these geometries in the microscopic world by designing molecules with pyramidal shapes.
CHEM 1201 Lecture Notes Summer 2014, Lecture 9 Electronegativity
Due to its five valence electrons,.
When all three atoms at the corners are identical the.
We can use the vsepr model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring all other. In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base, resembling a tetrahedron (not to be confused with the. The trigonal pyramidal arrangement of amines and ammonia is slightly flattened, with a lone pair of electrons above the nitrogen atom. Among these, the trigonal pyramidal.
In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base. The trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry of nh 3 is an example of tetrahedral electron pair geometry resulting in trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. What is a trigonal pyramidal arrangement?